算法 算法日记 FANSEA 2023-11-08 2024-10-31 算法日记 时间复杂度与空间复杂度 时间复杂度与空间复杂度详解 —— 如何计算 + 如何表示_空间复杂度和时间复杂度-CSDN博客
时间复杂度:循环(执行)次数
空间复杂度:栈帧的开辟数量,常量的数量
N次循环,如果每次循环都会创建一个新的常量则为 O(N)
Java数据结构API Stack Java Stack 类 |菜鸟教程 (runoob.com)
1 Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack <Integer>();
peek 查看最顶部元素pop 弹出最顶部元素push 将元素压入栈中
降序排序 1 Arrays.sort(arr, (a, b) -> b - a);
int数组降序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.List;public class DescendingSortExample { public static void main (String[] args) { Integer[] numbers = {5 , 3 , 8 , 1 , 2 , 9 , 4 , 7 , 6 }; List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(numbers); Collections.sort(list, Collections.reverseOrder()); numbers = list.toArray(new Integer [0 ]); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers)); } }
升序排序 1 Arrays.sort(arr, (a, b) -> a - b);
二分法查找 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 package test.Sorting;import static java.lang.Math.floor;class BinarySearch { public static int [] nums = {1 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,8 ,15 ,23 ,31 ,56 ,94 ,106 }; public static int search (int [] nums, int target) { int i = 0 ; int j = nums.length - 1 ; while (true ){ if (i>j){ return -1 ; } int m = (int ) (i+j)/2 ; int A = (int ) nums[m]; if (target < A){ j = m - 1 ; continue ; } else if (target > A) { i = m +1 ; continue ; }else { return m; } } } public static void main (String[] args) { int targetIndex = search(nums, 15 ); System.out.println("targetIndex = " + targetIndex); } }
两数之和
两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
示例 :
1 2 3 输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 输出:[0,1] 解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i< nums.length; i++) { if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) { return new int [] {map.get(target-nums[i]),i}; } map.put(nums[i], i); } throw new IllegalArgumentException ("No two sum solution" ); } }
回文数
这个首位调换很巧妙
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome (int x) { if (x < 0 ) return false ; int cur = 0 ; int num = x; while (num != 0 ) { cur = cur * 10 + num % 10 ; num /= 10 ; } return cur == x; } }
回文字符串 回文字符串
回文字符串所用API:
static boolean isLetterOrDigit(char ch)判断字符是不是字母或数字
static boolean isLetter(char ch)判断字符是不是字母
static boolean isDigit(char ch)判断字符是不是数字
static char toLowerCase(char ch)将大写字符转换成小写字符
static char toUpperCase(char ch) 将小写字符转化成大写字符
还有将字符串里的字符全部转换的方法
String toLowerCase()转小写
String toUpperCase()转大写
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public boolean isPalindrome (String s) { StringBuffer sgood = new StringBuffer (); int length = s.length(); for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) { char ch = s.charAt(i); if (Character.isLetterOrDigit(ch)) { sgood.append(Character.toLowerCase(ch)); } } StringBuffer sgood_rev = new StringBuffer (sgood).reverse(); return sgood.toString().equals(sgood_rev.toString()); } }
简单排序算法 定义工具类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class Util { public static boolean greater (Comparable v,Comparable w) { return v.compareTo(w)>0 ; } public static void exchange (Comparable[] a,int i,int j) { Comparable temp; temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; } }
冒泡排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 package test.Sorting;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.List;public class Bubbling { public static void sort (Comparable[] a) { for (int i = a.length-1 ;i>0 ;i--){ for (int j = 0 ;j<i;j++){ if (Util.greater(a[j],a[j+1 ])){ Util.exchange(a,j,j+1 ); } } } } public static void main (String[] args) { Integer[] arr = {-1 ,1 ,3 ,9 ,-85 ,8 ,4 ,6 }; sort(arr); System.out.println("arr = " + Arrays.toString(arr)); } }
选择排序
外循环次数:length
内循环次数:length - i
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public static void SelectSort (Comparable[] a) { for (int i= a.length;i>0 ;i--){ int minIndex = a.length-i; for (int j=a.length-i;j<a.length;j++){ if (Util.greater(a[minIndex],a[j])){ minIndex = j; } } Util.exchange(a,minIndex, a.length-i); } }
插入排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public static void injectSort (Comparable[] a) { for (int i = 0 ;i<a.length-1 ;i++){ for (int j = i+1 ;j>=1 ;j--){ if (Util.greater(a[j-1 ],a[j])){ Util.exchange(a,j-1 ,j); } } } }
高级排序算法 希尔排序 时间复杂度:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public static void hillSort (Comparable[] a) { int h = 1 ; while (h< a.length/2 ){ h=2 *h+1 ; } while (h>=1 ){ for (int i=h;i<a.length;i++){ for (int j=i;j>=h;j-=h){ if (Util.greater(a[j-h],a[j])){ Util.exchange(a,j,j-h); }else { break ; } } } h=h/2 ; } }
快速排序 时间复杂度:
选取左右指针,左指针用来确定需要指定移动的标准,右指针代表需要进行移动的数,期间左右指针会更换角色
合并两个有序链表 合并两个有序链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode dum = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode cur = dum; while (list1!=null && list2!=null ){ if (list1.val>list2.val){ cur.next = list2; list2 = list2.next; }else { cur.next = list1; list1 = list1.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = list1 != null ? list1 :list2; return dum.next; }
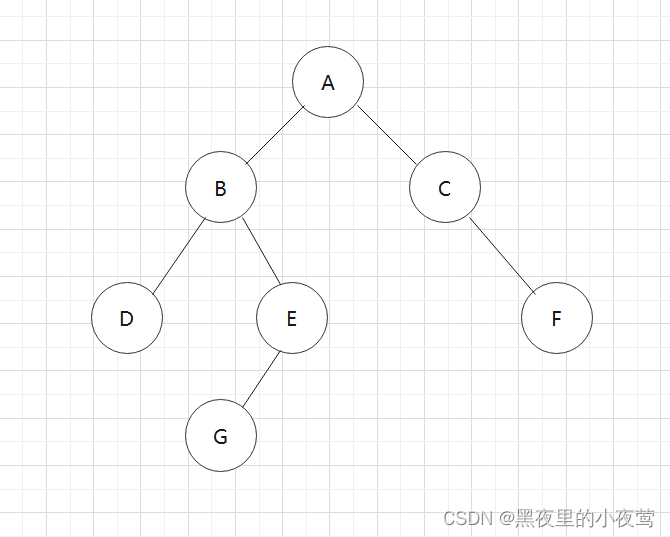
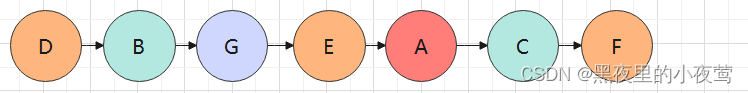
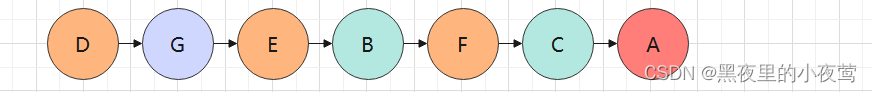
树的遍历(递归)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public void preOrderTraversal (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return ; } System.out.print(root.val + " " ); preOrderTraversal(root.left); preOrderTraversal(root.right); } public void inOrderTraversal (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return ; } inOrderTraversal(root.left); System.out.print(root.val + " " ); inOrderTraversal(root.right); } public void postOrderTraversal (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return ; } postOrderTraversal(root.left); postOrderTraversal(root.right); System.out.print(root.val + " " ); }
前序遍历 :
中序遍历 :
后序遍历 :
移动零(双向指针) 在利用双指针算法解题时,考虑原问题如何用暴力算法解出,观察是否可构成单调性,若可以,就可采用双指针算法对暴力算法进行优化!
283. 移动零
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
请注意 ,必须在不复制数组的情况下原地对数组进行操作。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: nums = [0,1,0,3,12] 输出: [1,3,12,0,0]
示例 2:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int m = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ if (nums[i]!=0 ){ exchange(nums,m,i); m++; } } } void exchange (int [] nums,int i,int j) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; }
除空格打印(双指针) 先看这样一个例子:输入一个字符每个子串之间有一个空格,让你输出每一个空格后的子串。
输入
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); String str = scanner.nextLine(); scanner.close(); int n = str.length(); int start = 0 ; int end = 0 ; while (start < n) { while (end < n && str.charAt(end) != ' ' ) { end++; } System.out.println(str.substring(start, end)); start = end + 1 ; if (end == n) { break ; } } } }
三数之和(双指针) 5. 三数之和
给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] 满足 i != j、i != k 且 j != k ,同时还满足 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 。请
你返回所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意: 答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4] 输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]] 解释: nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2] = (-1) + 0 + 1 = 0 。 nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[4] = 0 + 1 + (-1) = 0 。 nums[0] + nums[3] + nums[4] = (-1) + 2 + (-1) = 0 。 不同的三元组是 [-1,0,1] 和 [-1,-1,2] 。 注意,输出的顺序和三元组的顺序并不重要。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList <>(); Arrays.sort(nums); int n = nums.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 2 ; i++){ if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]) { continue ; } int left = i+1 ; int right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left<right){ if (nums[left]+nums[i]+nums[right]==0 ){ list.add((Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]))); while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1 ]) { left++; } while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1 ]) { right--; } left++; right--; } if (nums[left]+nums[i]+nums[right]<0 ){ left++; }else if (nums[left]+nums[i]+nums[right]>0 ){ right--; } } } return list; }
走方格(动态规划)
在for循环中不断执行动态转移函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public class FindWay { static int [][] arr = new int [30 ][30 ]; public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); int n = scanner.nextInt(); int m = scanner.nextInt(); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++){ if (i == 1 && j == 1 ){ arr[i][j] = 1 ; continue ; } if ((i&2 )==0 && (j&2 )==0 ){ continue ; } arr[i][j] = arr[i-1 ][j] + arr[i][j-1 ]; } } System.out.println(arr[n][m]); return ; } }
句子反转(String应用) 题目描述:
给定一行句子,每个词之间用空格隔开,要么是全小写英文单词,要么是全大写英文单词,要么是自然数。
要求将这些单词倒序输出。而且对于每个单词,如果是小写词,应当转为大写;如果是大写词,应当转为小写;如果是自然数,应该倒转输出。
举一个例子:
1 we choose TO go 2 the 123 moon
程序应当输出:
1 MOON 321 THE 2 GO to CHOOSE WE
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); String sentence = scanner.nextLine(); List<String> words = new ArrayList <>(); for (String word : sentence.split(" " )) { words.add(word); } Collections.reverse(words); for (String word : words) { if (word.matches("[a-z]+" )) { System.out.print(word.toUpperCase() + " " ); } else if (word.matches("[A-Z]+" )) { System.out.print(word.toLowerCase() + " " ); } else { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (word); sb.reverse(); System.out.print(sb.toString() + " " ); } } scanner.close(); } }
前缀数和 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); int [] arr=new int []{1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 }; int [] sum = new int [6 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < arr.length+1 ; i++) { sum[i]=sum[i-1 ]+arr[i-1 ]; } for (int i = 0 ; i < sum.length; i++) { System.out.println(sum[i]); } int L = scanner.nextInt(); int R = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.println("[L,R]的区间和:" +(sum[R+1 ]-sum[L])); scanner.close(); }
给定 $n$ 个整数 $a_{1}, a_{2}, \cdots, a_{n}$, 求它们两两相乘再相加的和,即
$$
样例输入:
样例输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); int n = scanner.nextInt(); int [] arr = new int [n]; long sum = 0 ; long ans = 0 ; long cns = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { arr[i] = scanner.nextInt(); sum+=arr[i]; } for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { sum-=arr[i]; ans+=arr[i]*sum; } System.out.println(ans); scanner.close(); } }
K倍区间 :
[P8649 蓝桥杯 2017 省 B] k 倍区间 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); int N = scanner.nextInt(); int K = scanner.nextInt(); long [] prefixSum = new long [N + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= N; i++) { prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1 ] + scanner.nextLong(); } Map<Integer, Integer> modCount = new HashMap <>(); modCount.put(0 , 1 ); long kMultipleIntervalCount = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= N; i++) { int mod = (int ) (prefixSum[i] % K); kMultipleIntervalCount += modCount.getOrDefault(mod, 0 ); modCount.put(mod, modCount.getOrDefault(mod, 0 ) + 1 ); } System.out.println(kMultipleIntervalCount); scanner.close(); } }
递增三元组 [P8667 蓝桥杯 2018 省 B] 递增三元组 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 public class Main { public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); int n = scanner.nextInt(); int [] a = new int [n]; int [] b = new int [n]; int [] c = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < a.length; i++) { a[i] = scanner.nextInt(); } for (int i = 0 ; i < b.length; i++) { b[i] = scanner.nextInt(); } for (int i = 0 ; i < c.length; i++) { c[i] = scanner.nextInt(); } Arrays.sort(a); Arrays.sort(b); Arrays.sort(c); int [] B = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int left=0 ,right=n-1 ; while (left>right) { int mid = (left+right)/2 ; if (c[mid]>b[i]) { right = mid; }else { left = mid+1 ; } } if (c[left]>b[i]) { B[i] = n-left; } } long [] sum = new long [n+1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < sum.length; i++) { sum[i] = sum[i-1 ]+B[i-1 ]; } long ans = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int left=0 ,right=n-1 ; while (left>right) { int mid = (left+right)/2 ; if (b[mid]>a[i]) { right = mid; }else { left = mid+1 ; } } if (b[left]>a[i]) { ans+=sum[n]-sum[left]; } } System.out.println(ans); scanner.close(); } }
全排序(DFS)
按照字典序输出自然数 11 到 n 所有不重复的排列,即 n 的全排列,要求所产生的任一数字序列中不允许出现重复的数字。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 package leetCode;import java.util.*;public class Main { static List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList <>(); public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); int n=scanner.nextInt(); int [] v=new int [n+1 ]; List<Integer> t = new ArrayList <Integer>(); dfs(n, v, t); for (int i = 0 ; i < list.size(); i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < list.get(i).size(); j++) { System.out.print(list.get(i).get(j)+" " ); } System.out.println(); } scanner.close(); } public static void dfs (int n,int [] v,List<Integer> t) { if (t.size()== n) { list.add(new ArrayList <>(t)); return ; } for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++) { if (v[i]==1 )continue ; v[i] = 1 ; t.add(i); dfs(n,v,t); v[i] = 0 ; t.remove(t.size()-1 ); } } }
危险系数 [P8604 蓝桥杯 2013 国 C] 危险系数 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
数组的划分(DFS+剪枝) [P1025 NOIP2001 提高组] 数的划分 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class Main { static int n,k,ans = 0 ; public static void main (String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); n = scanner.nextInt(); k = scanner.nextInt(); dfs(1 ,0 ,0 ); System.out.println(ans); scanner.close(); } static void dfs (int last,int sum,int cnt) { if (cnt==k) { if (sum==n) { ans++; } return ; } for (int i = last; sum+i*(k-cnt)<=n; i++) { dfs(i, sum+i, cnt+1 ); } } }
过河卒问题(DP) [P1002 NOIP2002 普及组] 过河卒 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 package leetCode;import java.util.*;public class Main { public static void main (String args[]) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); int [][] arr = new int [23 ][23 ]; int n = scanner.nextInt(); int m = scanner.nextInt(); int x = scanner.nextInt(); int y = scanner.nextInt(); arr[0 ][0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { if (ifControll(0 , i, x, y)) { break ; } arr[0 ][i] = 1 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { if (ifControll(i, 0 , x, y)) { break ; } arr[i][0 ] = 1 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) { if (!ifControll(i, j, x, y)) { arr[i][j] = arr[i-1 ][j] + arr[i][j-1 ]; }else { arr[i][j] = 0 ; } } } System.out.println(arr[n][m]); scanner.close(); } public static boolean ifControll (int i,int j,int x,int y) { if ((Math.abs(x-i)==2 &&Math.abs(y-j)==1 )||(Math.abs(x-i)==1 &&Math.abs(y-j)==2 )) { return true ; } return false ; } }
记忆化搜索 [T174480 【例题】NOIP2001 普及组] 数的计算 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 package leetCode;import java.util.*;public class Main { static int [] arr = new int [100 ]; public static void main (String args[]) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in); int n = scanner.nextInt(); System.out.println(func(n)); scanner.close(); } static int func (int n) { if (arr[n]!=0 ) { return arr[n]; } int count = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n/2 ; i++) { count+=func(i); } arr[n] = count; return count; } }
动态规划 746. 使用最小花费爬楼梯 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
在代码开头列举可以直接得出的结果返回
理解题意,初始化dp的值
通过动态转移方程,遍历到题中所需要的情况
返回dp[length]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int minCostClimbingStairs (int [] cost) { if (cost.length <= 1 ) { return 0 ; } int [] dp = new int [cost.length+1 ]; dp[1 ] = 0 ; dp[2 ] = Math.min(cost[0 ], cost[1 ]+dp[1 ]); for (int i = 3 ; i <= cost.length; i++) { dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ]+cost[i-1 ], dp[i - 2 ]+cost[i-2 ]); } return dp[cost.length]; } }
BFS(广度优先)
由点及面遍历,如果能走的通,则将元素压入队列尾部。如果队列不为空则一直循环,从队头扩散
DFS(深度优先)
从某一个点出发,递归调用方法按顺序走上下左右四个方向,由于递归的回溯性,一条路走到底后会在原先的途经点继续搜索可循路径
LRU
哈希表和链表映射
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 public class LruCache { public LruCache (int maxSize) { MAX_SIZE = maxSize; } public static class CacheObj { String key; String value; public CacheObj (String key, String value) { this .key = key; this .value = value; } } private final int MAX_SIZE; public final Map<String, CacheObj> cacheMap = new HashMap <>(); public final LinkedList<CacheObj> cacheLinked = new LinkedList <>(); public void put (String key, String value) { CacheObj cacheObj = new CacheObj (key, value); if (cacheMap.size()>=MAX_SIZE){ cacheMap.remove(cacheLinked.getLast().key); cacheLinked.removeLast(); } cacheMap.put(key, cacheObj); cacheLinked.addFirst(cacheObj); } public String get (String key) { if (! cacheMap.containsKey(key)) { return null ; } CacheObj cacheObj = cacheMap.get(key); cacheLinked.remove(cacheObj); cacheLinked.addFirst(cacheObj); return cacheObj.value; } public static void main (String[] args) { LruCache lruCache = new LruCache (5 ); lruCache.put("1" , "1" ); lruCache.put("2" , "2" ); lruCache.put("3" , "3" ); lruCache.put("4" , "4" ); lruCache.put("5" , "5" ); lruCache.put("6" , "6" ); lruCache.put("1" , "2" ); for (CacheObj cacheObj : lruCache.cacheLinked) { System.out.println(cacheObj.key + " : " + cacheObj.value); } } }
贪心算法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); // Read number of tables and batches int numTables = scanner.nextInt(); int numBatches = scanner.nextInt(); // Read max capacity per table Integer[] capacities = new Integer[numTables]; for (int i = 0; i < numTables; i++) { Integer x = scanner.nextInt(); capacities[i] = x; } // Store batches as pairs of customer count and expected revenue List<int[]> batches = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < numBatches; i++) { int customers = scanner.nextInt(); int revenue = scanner.nextInt(); batches.add(new int[]{customers, revenue}); } // 使用自定义比较器进行降序排序 Arrays.sort(capacities,(a,b)-> b-a); // Sort batches by descending order of revenue batches.sort((a, b) -> Integer.compare(b[1], a[1])); int totalRevenue = 0; // Try to assign each batch to a suitable table for (int[] batch : batches) { int customers = batch[0]; int revenue = batch[1]; for (int i = 0; i < numTables; i++) { if (capacities[i] >= customers) { totalRevenue += revenue; capacities[i] = customers; break; } } } System.out.println("Total Revenue: " + totalRevenue); }
思考题 8大排序算法的稳定和不稳定分析? 稳不稳定取决于:能否保证排序前2个相等的数其在序列的前后位置顺序和排序后它们两个的前后位置顺序相同。在简单形式化一下,如果Ai = Aj,Ai原来在位置前,排序后Ai还是要在Aj位置前。
不稳定 :选择排序、快速排序、希尔排序、堆排序稳定 :冒泡排序、插入排序、归并排序、基数排序